Location: Nigeria// Organization: KNCV Nigeria
Introduction
The combined maximum capacity of two major correctional centers in Oyo State is 590 inmates. However, the actual inmate population has exceeded 1,500, significantly increasing the risk of TB spread among inmates. Consequently, the project introduced the shift from passive to active case-finding in these correctional centers.
Intervention
- From January 2019 to December 2021 (36 months), passive case-finding was conducted in two correctional centers.
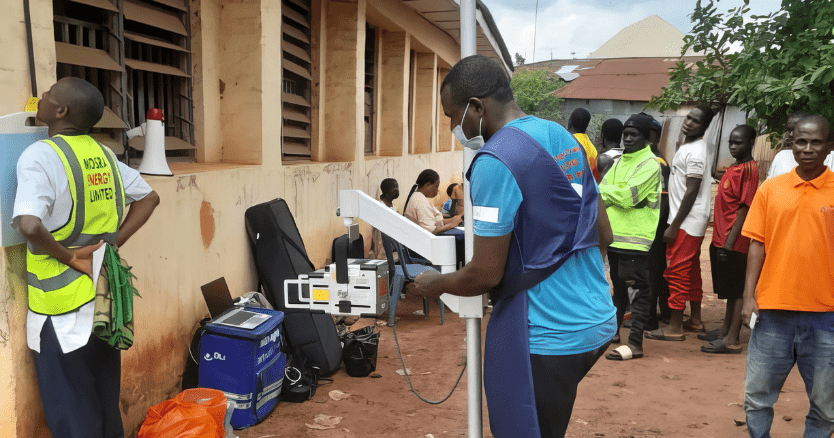
- Starting January 2022 and continuing until December 2023 (24 months), routine TB screening was implemented using both the WHO 4-symptom screen (W4SS) and portable digital X-ray machines Delft Light equipped with AI-powered CAD4TB.
- Presumptive TB cases were further tested using GeneXpert. X-ray images with high CAD4TB scores but bacteriologically negative were reviewed by a radiologist.
Result
- During the period from 2019 to 2021 (36 months), 4,500 inmates were screened, leading to the identification of 71 TB cases.
- In the subsequent period from 2022 to 2023 (24 months), 3,200 inmates were screened using both W4SS and Delft Light with CAD4TB, identifying 239 TB cases.
- This indicates a 237% increase in TB case detection when combining symptom screening with X-ray and AI, despite the shorter time frame.
Conclusion
- Active case-finding through combining W4SS and portable X-ray machines with CAD4TB significantly enhanced TB case detection in correctional centers.
- These results underscore the importance of addressing the challenges associated with TB spread among inmates.
REFERENCE: Ajayi, O. et al (2024, November 12-16). Role of active case finding and artificial intelligence in significantly increased TB case finding numbers in correctional centers: USAID TB-LONG3 project experience in Oyo State [Presentation]. The Union World Conference on Lung Health, Bali, Indonesia.