Source: Dr Alex Scott’s presentation “Can AI-driven computer-aided detection optimize X-pert-oriented community-based active case finding for TB? An interim trial progress report”// Location: South Africa // Organization: The Union World Conference 2024
Introduction
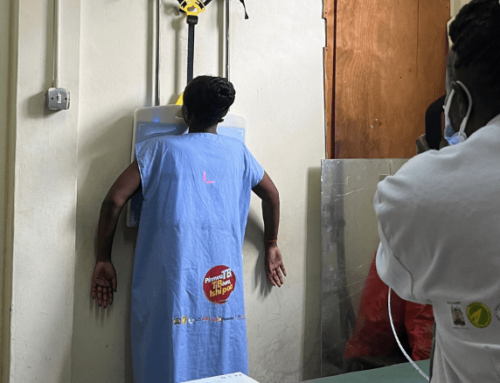
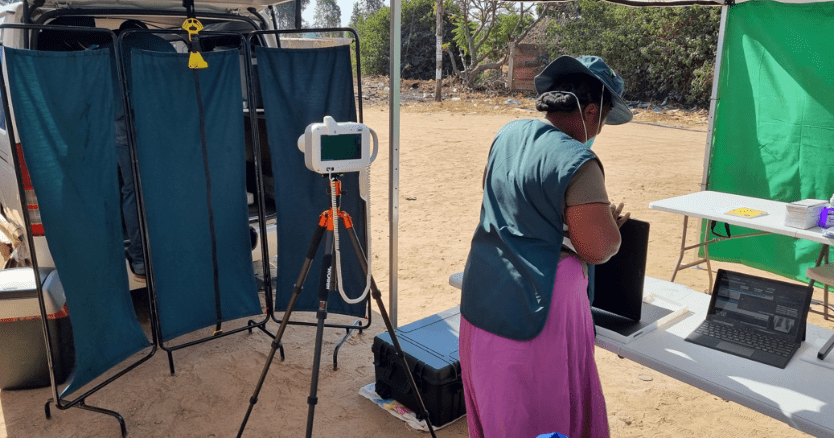
Community-based Active Case Finding (ACF) is crucial for identifying undiagnosed TB cases, including those without symptoms who may contribute to community-based transmission. The XACT-19 project incorporates ultra-portable X-rays with CAD/AI to enhance TB detection in the community.
Intervention
- The study employed an ultra-portable X-ray, Delft Ultra, with CAD4TB v7 in South Africa, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. It targeted high-risk groups, including symptomatic individuals, PLWH, those with previous TB, diabetics, and contacts of TB patients.
- Participants were divided into two arms: CAD4TB + Xpert (Arm 1) and Xpert only (Arm 2).
Result
- The interim results showed a 3.8% yield of total TB-positive cases (118/3,102), with 50.8% (60/118) asymptomatic. Among the Bac+ cases, 20% of asymptomatic individuals were found to be infectious.
- The study highlighted an instance of a relatively healthy, asymptomatic individual who was TB-positive, suggesting this person could be unknowingly transmitting the disease in the community.
Conclusion
- The XACT-19 project demonstrated the effectiveness of using Delft Ultra with CAD4TB in detecting high TB burden settings, suggesting a significant minority (~20%) was probably infectious, with a large proportion asymptomatic.
- These findings inform future ACF strategies in high TB burden settings, which is key for implementing strategies to detect TB in the community using these tools.
REFERENCE: Scott, A. et al (2024, November 12-16). Can AI-driven computer-aided detection optimize X-pert-oriented community-based active case finding for TB? An interim trial progress report [Presentation]. The Union World Conference on Lung Health, Bali, Indonesia.