Our projects in lung health
Zambia has been one of the earliest adopters of innovative TB screening technology. In 2023, the country recorded an estimated 60,000 TB cases, with nearly 9,000 TB-related deaths. Around 9,200 people remained missing from care, and 2,300 cases involved co-infection with HIV. The numbers underscore the need for ongoing efforts in active case finding, particularly among high-risk and hard-to-reach populations.
In 2009, we installed our first semi-mobile X-ray system at Kanyama Clinic in Lusaka. Serving one of the busiest HIV/TB clinics in Zambia, the system provided free imaging services to a catchment of around 200,000 people, many of whom lacked access to diagnostic care.
A year later, in 2010, we delivered the first Delft OneStopTB X-ray Truck for a TB Reach project executed by the Center of Infectious Disease and Research in Zambia (CIDRZ). The clinic included a digital X-ray unit, CAD4TB, and a TB smear microscopy lab, and was deployed in four Zambian prisons. This marked one of the earliest examples of integrating digital solutions for fast and cost-effective TB screening.
In 2011, CAD4TB was introduced in a TB Reach-funded project by Zambart. Used as a triage solution ahead of confirmatory tests, CAD4TB helped identify more TB cases at a lower cost. Results from the project showed a strong correlation between abnormal CAD4TB scores and positive confirmatory test results.

In 2017, we leased a Delft OneStopTB X-ray truck to CIDRZ, equipped with our EasyDR digital X-ray and CAD4TB software. A year later, we delivered a containerized clinic to FHI360 under the Challenge TB project and supplied 4 more of these mobile clinics through an EDCTP grant, two of which were deployed in Zambia by Zambart.
In 2019, PATH procured a Delft OneStopTB X-ray Trucks under the Eradicate TB Project funded by USAID. That same year, CIDRZ received 3 additional CAD4TB solutions to support their screening work.
Between 2020 and 2021, 6 more CAD4TB systems were deployed in mobile clinics across the country. In early 2021, we also provided CIDRZ with 3 Delft Light portable X-ray systems to expand reach in remote areas.
Most recently, in 2025, another CAD4TB system was delivered to CIDRZ to continue supporting their nationwide efforts in TB detection.
Our projects in maternal health
Zambia has significantly reduced maternal mortality, reporting 85 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2023. This figure reflects a substantial decline from 596 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2000, signaling national progress in maternal health services. Nonetheless, disparities remain between urban and rural access to antenatal care and diagnostic imaging, particularly for early risk detection during pregnancy.
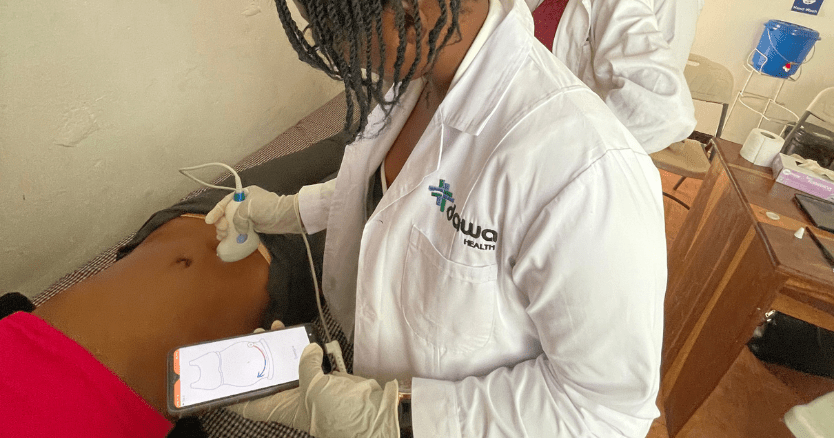
In 2023, we deployed four BabyCheckers in Zambia with Dawa Health. Since then, they have assisted healthcare workers in facilitating early detection and referral, especially in hard-to-reach areas of Lusaka and border areas of Zimbabwe.
Making a difference
Lung health
Research paper
In 2013, a study was published on detecting tuberculosis using automated reading (utilizing the CAD4TB artificial intelligence solution). The study should show that the assessment of chest X-rays using CAD4TB and by clinical officers was comparable and that CAD4TB had the potential as a point-of-care test and for the automated identification of subjects who require further examinations. Note that this study used a significantly older version of CAD4TB than currently available.
In 2014, another study was published looking at the utilization of CAD4TB in Lusaka, Zambia. It showed that the use of CAD with digital chest X-ray has the potential to increase the use and availability of chest radiography in screening for TB where trained human resources are scarce.
In 2017, a study looked at using digital chest X-rays with computer-aided diagnosis software (CAD4TB) versus symptom screening to define tuberculosis among household contacts and the impact on tuberculosis diagnosis. The study showed that symptom screening if used alone with follow-on definitive TB testing, would have led to missing eight of the 19th confirmed TB cases, and CAD software could support TB screening efforts.
CAD4TB was reviewed as part of the Zambia National Tuberculosis Prevalence Survey that same year. A study on this objective looked at the performance of the CAD4TB software against that of field- and central readers. The performance of CAD4TB was similar to that of field and central readers. The study concluded that the performance of automatic chest X-ray readings is comparable to that of human experts in a TB prevalence survey setting using culture as a reference.
Later, in 2021, one study was published on the costs and cost-effectiveness of a comprehensive tuberculosis case-finding strategy in Zambia, also considering CAD4TB.
That same year, a study looked at using CAD as a triage test for pulmonary tuberculosis and found that CAD-based chest X-ray analysis can be implemented as a high-sensitivity tuberculosis rule-out test.
In 2022, a study reviewed the performance of computer-aided detection digital chest X-ray reading technologies (CAD4TB) for the triage of active tuberculosis among persons with a history of previous tuberculosis. It showed that CAD4TB achieved a sensitivity and specificity of 89.3% and 24%, and 90.5% and 60.3% amongst those with and without previous TB, respectively.
In 2023, a study assessed non-tuberculosis abnormalities on digital chest X-rays with high CAD4TB scores using data from a tuberculosis prevalence survey in Zambia and South Africa. The study found that a wide range of non-TB abnormalities can be identified on digital chest X-rays among individuals with high CAD4TB scores but do not have bacteriologically confirmed TB. A tool like CAD4TB could simultaneously identify other causes of abnormal chest X-rays alongside TB, which could be interesting for future research.
Case study
As part of the Eradicate TB Project, Zambia’s Copperbelt Province – the country’s highest TB burden region – implemented the Mobile OneStopTB (MOST) Clinic to intensify TB case finding at 30 identified hotspots. The intervention led to a 49 percent increase in TB case notifications, demonstrating the effectiveness of mobile clinics in reaching underserved communities. Expanding the MOST clinic model to other provinces holds potential for closing the gap between estimated incidence and reported TB cases. The case study was presented by Onety Hanyuma of PATH Zambia during the 52nd Union World Conference on Lung Health, 2021.
The XACT-19 project evaluated the use of Delft Ultra with CAD4TB v7 in South Africa, Zambia, and Zimbabwe to enhance TB detection through community-based Active Case Finding (ACF). Targeting high-risk groups, the study compared a CAD4TB + Xpert approach against Xpert-only screening. Interim findings revealed a TB positivity rate of 3.8 percent, with over half of the detected cases being asymptomatic. Notably, 20 percent of these asymptomatic individuals were found to be infectious. These results underscore the role of AI-enabled diagnostics in identifying undetected TB transmission. The case study was presented by Dr. Alex Scott at the Union World Conference on Lung Health in Bali, November 2024.
The Ubumi Bwandi project in Zambia explored the effectiveness of CAD4TB in community-wide TB screening across urban settings. By comparing triage and parallel screening algorithms, the project found that 94 percent of TB cases had CAD4TB scores of 50 or higher, with over a quarter of those individuals showing no symptoms. Parallel screening resulted in higher detection rates, while triage led to a 30–40 percent decrease in TB diagnoses. These results highlight the value of AI-driven diagnostics in improving TB case finding among asymptomatic individuals. The case study was presented by Anton Schaap at the Union World Conference on Lung Health in Bali, November 2024.
Webinar insights
In urban and peri-urban communities with high HIV prevalence, the TREAT Study conducted a TB prevalence survey using the OneStopTB Clinic as a mobile field site. Equipped with digital X-rays, CAD4TB with cloud access, and an onboard laboratory, the clinic enabled same-day screening and diagnosis without requiring sample transport. The use of CAD4TB supported not only TB detection but also identification of non-TB abnormalities. This approach streamlined diagnostic workflows and enhanced case management. The case study was presented by Chali Wapamesa and Michael Burnett during Delft Imaging’s webinar on October 14, 2021.
During Delft Imaging’s March 2025 webinar, Prof. Helen Ayles presented “Ubomi Buandi” (“My Health, My Choice”), a community-centered model in Zambia that integrates TB screening with broader wellness services. Implemented in Ndola’s high-burden mining region, the initiative combines portable X-rays, CAD4TB, and a wide range of health screenings—including HIV, NCDs, and occupational lung diseases – through a dedicated Community Hub. With support from Delft and TB REACH, the model has improved early TB detection, identified post-TB lung conditions, and introduced incentives to promote screening participation.
Webinar insights
During the 2024 BabyChecker webinar, Tafadzwa Kalisto Munzwa, Co-founder and Executive Director at Dawa Health, presented how BabyChecker strengthens clinical decision-making and referral pathways. One highlighted case involved the early identification of a low-lying placenta, allowing for timely referral and critical care access.
This deployment approach emphasizes collaboration with community health workers to foster trust and ensure continuity of care. BabyChecker continues to enhance early detection of pregnancy-related risks in low-resource antenatal settings.